Overview
| Excerpt |
|---|
This article provides general tips to determine if a website is legitimate or secure. |
Is the Website Legitimate?
...
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
When trying to connect to an illegitimate website, your web browser may prompt you with an error message. If you receive a message like the one below, the website may not be legitimate. |
Is the Website Secure?
...
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
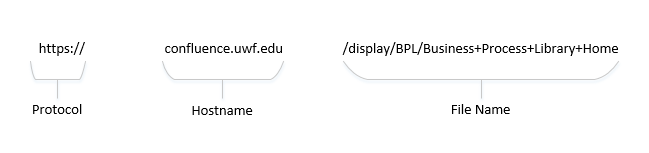
Web addresses are split into three different parts: the protocol (https://), the hostname (www.example.com), and the file name. If the protocol is "https" for a site, you are using a secure page. Below is an example of a secure URL: |
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
A website's Privacy Policy will state how data is collected on the company's website. If you're concerned about the data the website may be gathering, refer to their Privacy Policy. If you're unable to find the website's privacy policy, the site may not be secure. |
...
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Open an incognito window in Google Chrome. To open an incognito window in Windows, Linux, or Chrome OS: Press Ctrl + Shift + n. For Mac OS: Press ⌘ + Shift + n. . Next, paste the link in the address bar and press "Enter" to see if a login is required on the webpage. |
FAQs
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Some common web domains are:
If a website does not have one of these domains, it may not be secure or legitimate. This does not mean that websites with these domains are always secure or legitimate, these are only commonly used domains. International sites will often have a domain for their country (such as .uk). |
...