Overview
| Excerpt |
|---|
This article provides general tips to determine if a website is legitimate or secure. |
Is the Website Legitimate?
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
A domain name is the name of a website. For example, uwf.edu is a domain name. It's very difficult for scammers to create fake websites with https://uwf.edu as the domain name. But scammers can create websites that have URLs similar to the official address. Users must pay close attention:
|
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
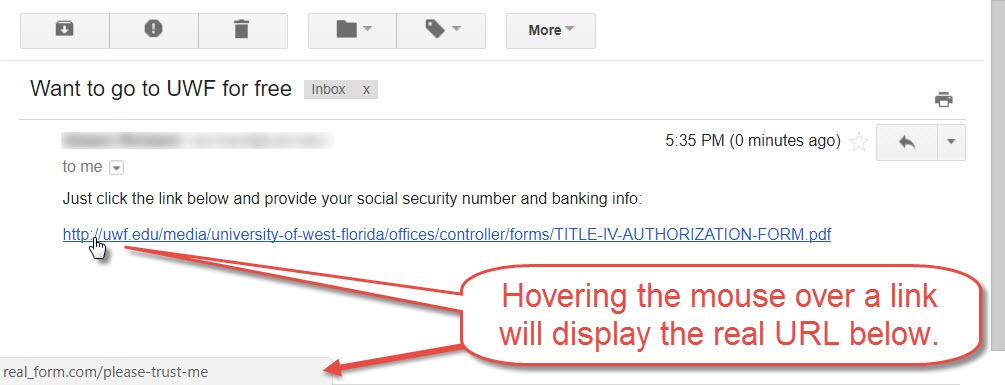
By checking the address bar, you can verify that the site you accessed did not "redirect" you to a different site. Some attackers will use a "redirect" method to gather data. When redirected, you may click or access a link for a known site and may be sent to another. For example, accessing Amazon should bring you to a website with the web address of "amazon.com." If the address bar shows a different website, the website may not be legitimate. Please see the FAQ for further information about web addresses. Also note you can hover over links on webpages and emails to see what their actual URLs are. See screenshot below for an example. |
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Many scammer realize that users accidentally mistype URLs. For example, some users will type gmial.com when trying to access Gmail. Scammers could then simply purchase the gmial.com domain for their website, and imitate Gmail's login screen. So when people go to gmial.com, see something that looks like Gmail, and provide their login credentials, now the scammers have compromised these users Gmail accounts. Simply put, always ensure that the URLs you visit are accurate. |
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Users may choose to shorten their links, so that they could fit those links in a 240-character Twitter post. But in most other instances, tiny links should be avoided, as character limits are usually not an issue, and you won't know where that tiny link leads until after you click it. Please note one major exception – tiny links to Confluence pages. This is an exception because users can tell where the link comes from; a tiny link from Confluence still begins with confluence.uwf.edu. But with most other tiny links, users can't tell where the original link came from (e.g., https://bit.ly/32uPBBt ← this link is safe). |
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Check the website itself before conducting business with the website. Usually, at bottom of a website, there is an option called "Contact Us." If you do not trust a website, contact the company using the contact information listed. If you do not receive a response (or you notice the phone number is out of service), the site may not be legitimate. |
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Legitimate businesses try to keep their websites professional in appearance and behavior. Check the website for things such as spelling errors, major grammatical errors, or readability ("Does the text make sense?"). Sites with these sorts of errors may not be legitimate. Trust your instincts. If the page does not look right, it may not be. |
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
A common method of investigating the legitimacy of a site is to use a major search engine (such as Google). Feel free to refer to VirusTotal's tool to check for possible vulnerabilities (use the "URL" tab to scan the site). |
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
When trying to connect to an illegitimate website, your web browser may prompt you with an error message. If you receive a message like the one below, the website may not be legitimate. |
Is the Website Secure?
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
If there is a 🔒 symbol located before the address in the address bar, you are using a private connection. If a website has private connections, it usually is a secure website. |
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
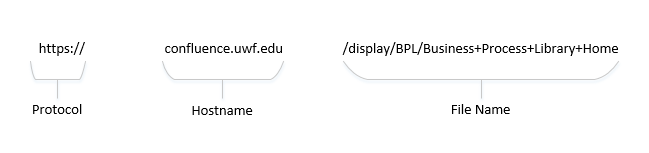
Web addresses are split into three different parts: the protocol (https://), the hostname (www.example.com), and the file name. If the protocol is "https" for a site, you are using a secure page. Below is an example of a secure URL: |
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
A website's Privacy Policy will state how data is collected on the company's website. If you're concerned about the data the website may be gathering, refer to their Privacy Policy. If you're unable to find the website's privacy policy, the site may not be secure. |
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Open an incognito window in Google Chrome. To open an incognito window in Windows, Linux, or Chrome OS: Press Ctrl + Shift + n. For Mac OS: Press ⌘ + Shift + n. . Next, paste the link in the address bar and press "Enter" to see if a login is required on the webpage. |
FAQs
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
No. Not all legitimate sites use or need to use a secure connection. This does not mean that you cannot trust a legitimate website, but you should exercise caution when using the site. |
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
No. Some sites will behave and look like a legitimate site, when in fact they are used to lure visitors to enter sensitive data. One example of these sorts of activities is a "man-in-the-middle attack." In this scenario, an attacker sets up a site that looks like its legitimate counterpart (such as a banking site). However, the site is designed to have the victim enter sensitive data (such as passwords, SSNS, etc) for the attacker to gather. For more information on man-in-the-middle attacks, please read TechTarget's article. |
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|